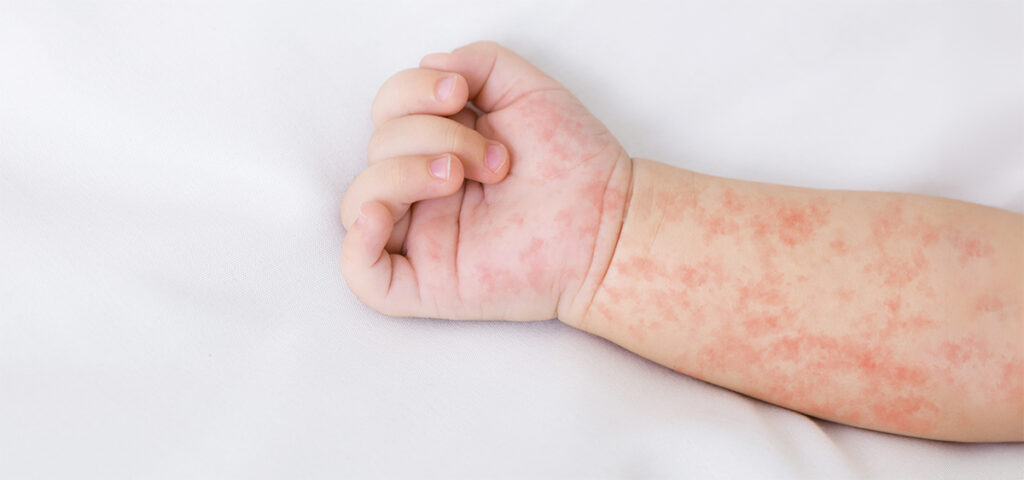
Once considered close to eradication in many parts of the world, measles is making a troubling comeback.
According to a joint report by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), measles cases increased by 20% globally in 2023, with an estimated 10.3 million infections and over 306,000 confirmed cases reported across 144 countries. This marks a significant rise from 8.65 million cases in 2022.
The United States CDC also reports an alarming rise in measles clusters, primarily due to low vaccination coverage and increased international travel.
What is Measles?
Measles is a viral disease caused by the measles virus, a member of the Paramyxoviridae family. It spreads through respiratory droplets and can linger in the air or on surfaces for hours.
Symptoms typically appear 7–14 days after exposure and include:
- High fever
- Cough, runny nose, and red, watery eyes
- Koplik spots (tiny white spots inside the mouth)
- A characteristic red rash that spreads from the face downward
Severe complications can include pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death, especially among malnourished children and immunocompromised individuals.
Why Are Cases Rising?
Several factors contribute to the current surge in measles cases:
- Declining vaccination rates:
Measles is preventable with two doses of the measles vaccine; yet more than 22 million children missed their first dose of the measles vaccine in 2023. Globally, an estimated 83% of children received their first dose of measles vaccine last year, while only 74% received the recommended second dose.
- Disrupted immunization programs due to COVID-19
- Misinformation about vaccine safety
- Global mobility and population displacement
The combination of high transmissibility (a single infected person can spread it to up to 18 others) and reduced herd immunity has created a perfect storm for outbreaks.
The Role of Accurate Diagnostics
Since the early symptoms of measles resemble other viral infections, laboratory confirmation is essential, especially in outbreak scenarios. Molecular diagnostic methods like Real-Time PCR enable the detection of measles virus RNA with:
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Rapid turnaround time
- Ability to detect low viral loads, even in early stages
These features make Real-Time PCR the gold standard in measles diagnostics, particularly in surveillance, outbreak management, and confirmation of imported cases.

How Anatolia Supports Measles Diagnostics
Anatolia offers advanced molecular testing tools designed to meet the demands of public health laboratories and clinical diagnostics. Bosphore Measles Virus Detection Kit v1 enables accurate, sensitive, and fast detection of the measles virus through Real-Time PCR technology. This kit can work from biological samples like nasopharyngeal aspirate, throat swab, nasopharyngeal swab, serum, plasma, and urine. The analytical detection limit was found to be 13 copies/reaction and 23 copies/reaction for the shorter thermal protocol.
With the increasing threat of vaccine-preventable diseases, timely and precise diagnosis remains a critical step toward protecting public health.




